Neural Networks — How do we train them with basic 3 layer?
The basis of any neural networks is the Perceptron. If you would like to know internal details of basic perceptron, I recommend reading first part of this article.
Perceptron — The brain behind Machine Learning
Now that you know what a perceptron is, you’re just one step from knowing what a neural network is.
A neural network is just a bunch of perceptrons organized in layers where the information of these perceptions is passed to the next layer.
Let us go one step ahead. We now know what perceptron looks like, we can consider a little more complex problem which has 2 perceptron which is fed to 1 perceptron and therefor gives the y^. The diagram looks something like this.
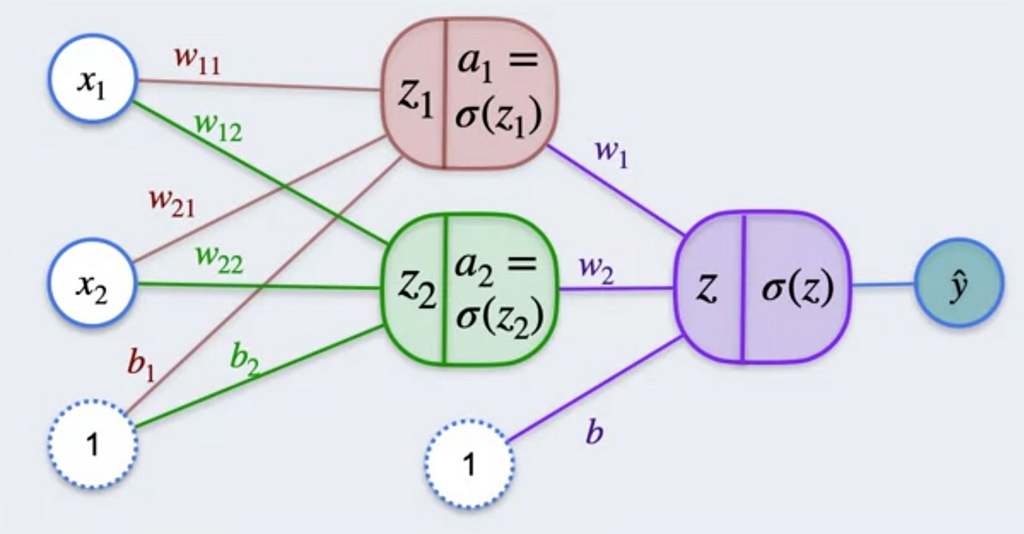
Here we have a₁ which is the activation function from z₁ and a₂, the activation function from z₂. The bias b is added to the z.
Now from the above diagram, we can infer that

Th z is the output of neural network. Now we can use Log loss and calculate the error. Now to minimize error we use Gradient descent and find the minimum loss of the neural networks
We know that the partial derivatives are required how the weights affect the loss or the error and in which direction the change would be.

In the above diagram, let us consider partial derivative of the y^ affected by w₁₁, we are showing what are the partial derivatives that affect the log loss and these are required for calculating the direction of loss if there is change in w₁₁. On calculating this, we get

From the above value, to find the optimal value of w₁₁ that gives least error. we perform gradient descent and the w₁₁ optimal value would be

similarly, for other value of weights and bias is calculated.
To summarize, Optimal value of weights and bias would be

So in short, if you do these updates for a learning rate alpha, you get better weights and biases. That’s how you update the first layer of the neural networks. For the second layer of neural networks, we follow the same process and using the above values we get.

This is the partial derivative of Log Loss with respect to w₁ and performing the gradient descent with w₁ will give optimal value of w₁.

To summarize, these are the values of w₁ , w₂ and b

This is how we train neural network with different values to give the optimal value.
How do we train our neural networks with the knowledge we gained?
Let us use little bigger neural network, now we use 3 layers. Superscript is used to represent the layer number like shown below.

Back Propagation is the method we use to train the neural networks.
The back propagation is the technique where we find the optimal values shown in the above diagram by calculating backwards. So, to start with we calculate the Loss from the partial derivatives of w for 3rd layer

similarly, for b in 3d layer. Now that we got the values, we go one step before and calculate the second layer which includes the chain rule that has already been done for the 3rd layer. So the values can be used and finally first layer which follows the same.
I know this process looks tedious, but in Machine learning, we don’t do these process manually for each layer and we use the tools to do that for us. But understanding of this concept can help us evaluate what the tool is doing and is it expected?
Reference: DeepLearning.ai
